|
Products-Industrial temperature sensor-MI RTDs-Tolerance, wiring method and temperature range
Tolerance of RTDs to Temperature and Applicable Standard Table
|
|
IEC 751
|
JIS C 1604
|
|
Class
|
Tolerance (℃)
|
Class
|
Tolerance (℃)
|
|
Pt100
( R(100℃) / R(0℃)=1.3851
|
A
|
±(0.15 +0.002|t|)
|
A
|
±(0.15 +0.002|t|)
|
|
B
|
±(0.3+0.005|t|)
|
B
|
±(0.3+0.005|t|)
|
Note.
1.Tolerance is defined as the maximum allowable deviation from the temperature vs resistance reference table.
2.l t l=modulus of temperature in degrees Celsius without regard to sign.
3. Accuracy class 1/n(DIN) refers to 1/n tolerance of class B in IEC 751
Wiring method of RTDs.
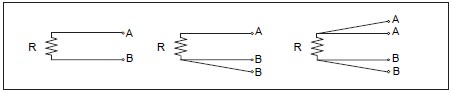
Two-conductor type:
Since a conductor resistance is added to the resistance value. It is necessary to reduce the conductor resistance in advance. This type is not usually used except for a high resistance RTDs.
Three-conductor type:
Use to eliminate the effect caused by conductor resistance. Care should be taken for long. Distance transmission because a variation of resistance of conductor has an effect on accuracy. This type of connection is widely used in industrial applications.
Four-conductor type:
This type of connection is used for high-accuracy measurement and standards because it is not affected by conductor resistance. Generally, a constant current is applied and the resistance value is measured by a potential difference.
MI RTD Operating Temperature Range
|
Symbol
|
Division
|
Operating temp range
|
|
L
|
For low temperature
|
-200~ +100
|
|
M
|
For medium temperature
|
0~350
|
|
H
|
For high temperature
|
0~550
|
|





